Why Y Chromosome Is Slowly Shrinking ? The Y chromosome, which is essential for determining male gender in humans and other mammals, is slowly deteriorating. If we do not develop a new sex gene, our species may disappear in a few million years, possibly resulting in our extinction. In this article we discuss about the reason and causes of Y chromosome is slowly shrinking.
A study published in 2022 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science demonstrates the evolution of a new gene responsible for determining male sex in the spiny rat.
Table of Contents
What is the Y Chromosome?
– The mechanism by which the Y Chromosome influences gender.
- Females possess two X chromosomes, whereas males carry one X chromosome and a smaller Y chromosome.
- The Y chromosome has a critical gene known as SRY (sex region on the Y) that initiates male development in embryonic stages.
- The activation of other genes by SRY, such as SOX9, is crucial in male determination in vertebrates.
– The vanishing Y Chromosome :
- The majority of mammals possess an X and Y chromosome system that is comparable to our own.
- Nevertheless, the platypus in Australia possesses sex chromosomes that are unique, similar to birds.
- Throughout 166 million years of evolution, approximately 900-55 active genes have been lost from the human Y chromosome.
- With the rate as it is now, the 55 remaining genes could vanish in 11 million years.
– Rodents lacking a Y chromosome:
– Certain rodent species, such as mole voles and spiny rats, have already lost their Y chromosome but are still able to thrive.
What are the implications of losing the Y chromosome?
Losing the Y chromosome could have diverse implications affecting individuals and the entire human population. Here are few important highlights:
Growth and maturation in males:
- The SRY gene, found on the Y chromosome, initiates male development in embryos.
- Absence of a functional Y chromosome would prevent male development, leading to an imbalance of sexes in the population.
Variety of genes within a population:
- The Y chromosome plays a role in genetic diversity by bringing about differences in genes specifically found in males.
- Losing it might lessen genetic diversity, which could make the population more vulnerable to diseases and shifts in the environment.
- Adaptations that have developed over time through the process of evolution.
- The Y chromosome has undergone changes over millions of years in response to varying environments.
- Losing it could restrict our capacity to adjust to upcoming challenges.
Sexual Health:
- Certain genes located on the Y chromosome are necessary for the production of sperm as well as for fertility.
- The lack of their presence could have an effect on the fertility of men.
Impacts on Society and Culture by Y chromosome is slowly shrinking :
- The Y chromosome is culturally important as a representation of manhood.
- Its vanishing could impact societal views on gender and norms.
Ongoing research efforts to address Why Y Chromosome Is Slowly Shrinking ?

The study of Y chromosome degeneration is a fascinating area of research. Let’s look into some revelations:
Study of the plant Rumex hastatulus:
- A recent research project examined the development of sex chromosomes in the dioecious plant Rumex hastatulus.
- The recently developed neo-sex chromosomes originated less than 200,000 years ago from vast genomic regions abundant in repeats and with minimal recombination.
- Nevertheless, the Y chromosome’s total lack of recombination resulted in more than 30% gene loss and substantial reorganization.
- Male genetic material is stored in the Y chromosome.
- In humans, the Y chromosome possesses mechanisms that hinder gene loss.
- Even without recombination advantages, genes on the Y chromosome continue to deteriorate as time passes.
- New studies indicate that gene loss rate may have come to a halt.
Continuing research on why Y chromosome is slowly shrinking :
- Scientists are still investigating the evolution of the Y chromosome, including the factors causing degeneration.
- Subjects covered are gene preservation, meiotic bias, and their effects on men’s well-being, such as cancer.
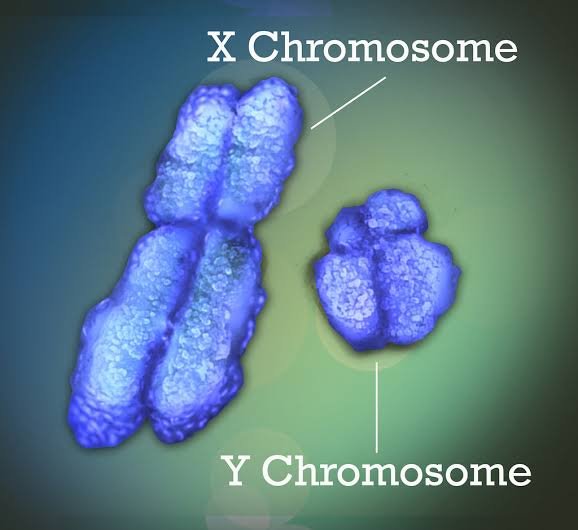
What are the differences between X and Y chromosomes?
Let’s examine the main difference between X and Y chromosomes.
Dimensions or measurements:
- The Y chromosome is shorter than the X chromosome.
Location of centromere:
- The centromere on the X chromosome is accurately positioned at the midpoint, known as metacentric.
- Y chromosome: Centromere located at one end (acrocentric).
- Being in a particular place or existing in a certain situation.
- X chromosomes are found in both males and females.
- Y chromosome is found solely in males.
Quantity of Copies:
- Females inherit two copies of the X chromosome, one from each parent.
- Males inherit one copy of the Y chromosome from their father.
Genes that are active.
- The X chromosome has a greater number of genes.
- Y chromosome has a lower number of genes.
Content of DNA:
- The X chromosome contains a greater amount of genetic material.
- The DNA content of the Y chromosome is lower.
Receiving wealth or property from a deceased relative:
- Genes on the X chromosome exhibit criss-cross inheritance.
- Genes on the Y chromosome exhibit direct inheritance.
Composition of chromatin:
- The X chromosome contains a higher proportion of euchromatin, which is DNA that is actively being transcribed.
- Y chromosome contains a higher amount of heterochromatin, which represents inactive DNA.
Operations; roles/tasks.
- The X chromosome plays a role in the formation of Barr bodies, the development of eggs, and other traits specific to females.
- The Y chromosome is essential for the development of males.
For more interesting update follow our official website.

